JavaScript is a class-free, object-oriented language, and as such, it uses prototypal inheritance instead of classical inheritance. 1
有几点关键的:
1.Javascript没有class的概念,在class based的语言中(Python,java,C++),开始先定义一个class,然后再跟进这个class实例化一个object。在JS中,object是从另一个object创建(不是实例化)的。
比如:
function Vehicle(hasEngine,hasWheels)
{
this.hasEngine = hasEngine || false;
this.hasWheels = hasWheels || false;
}
var v = Vehicle(true,true);
这里Vehicle是一个function object. v是一个通过这个function object创建的object.
Prototype构成了一个chain. 用于实现继承。比如
function Car(make,model,hp)
{
this.hp = hp;
this.make = make;
this.model = model;
}
Car.prototype = new Vehicle(true,true); //Car.prototype 指向Vehicle
Car.prototype.constructor = Car;//使得instance object的constructor指向Car
var car = new Car('audi','a6',120);
console.log(car.hasWheels) //这里输出true
这里是先创建了两个functions:Car和Vehicle, 并且把Vehicle作为Car的prototype.
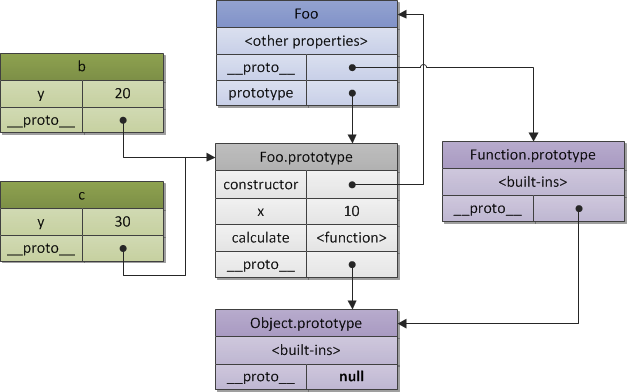
2.当一个function创建时,其prototype指向新创建对象的prototype。 比如:
function Foo(y) {
this.y = y;
};
Foo.prototype.x = 10;
// and inherited method "calculate"
Foo.prototype.calculate = function (z) {
return this.x + this.y + z;
};
var b = new Foo(20);
/*
Foo {y: 20, x: 10, calculate: function}
y: 20
__proto__: Foo
calculate: function (z) {...}
constructor: function Foo(y) {..}
x: 10
__proto__: Object
}
*/
var c = new Foo(30);
当前objects之间的关系是: